Command Widget¶
The widget enables the user to send a command with parameters to a certain device
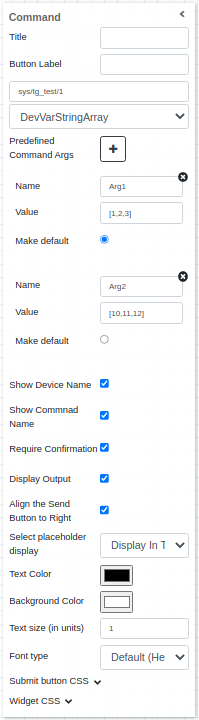
Widget setting¶
The user has the ability to select:
A free label for the widget (string), shown before devicename/command (leave blank to hide)
Button label (string), Submit as default value, the text of the button
Predefined Command Args, a way to define name, value pair as input/argument to the command
Show device name (boolean), if selected shows the name of the device following the format: device/command
Show command name (boolean) if selected shows the name of the command following the format: device/command
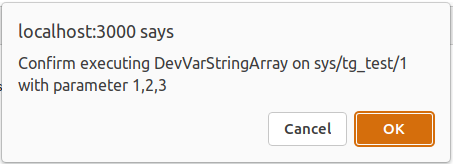
Require confirmation (boolean), shows a pop-up to the user to confirm to send the command
Display output (boolean), displays the output coming from TANGO
Text Color (color palette)
Background color (color palette)
Text size (integer)
Font type (dropdown menu)
Write custom CSS for the submit button
Write custom CSS for the widget container.
Widget input¶
Based on the type accepted to the command, the widget displays the input to send the argument to the device. The arguments accepted to the command are divided in thee type:
Void: If a command doesn’t accept arguments as input, means that it belongs to Void input type. So, the widget hides the input text.
Value: If a command accepts a Value as input, that should be an Float, String, Char and so on, the widget displays the input text where the user can insert the value to pass as argument.
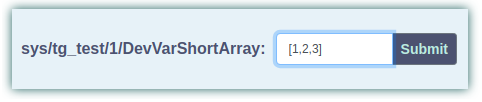
Array: If a command accepts an Array as input, the widget displays the text input where insert the array. The format must be: value1, value2, …., valueN, separated by commas and with “ or ‘, based on the type. Use ‘[]’ to pass an empty array. The widget converts the object in the input in a proper array, based on the input type accepted by the command, for example, it converts 0 in False if the input accepted is Boolean.
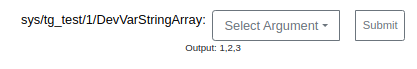
- Predefined Argument:A user can also define list of arguments for the widget during configuration phase. This can be done using
Predefined Command Argssection. The user can define the list of values (name-value pair) using plus+button. While defining the values, name field is optional; in such a case value would be used as name/label in the dropdown. During run mode these configured values are shown in a dropdown(instead of text input) from which user can select a value and execute the command.
- Predefined Argument:A user can also define list of arguments for the widget during configuration phase. This can be done using
User can click execute button or hit enter key to fire the command. A pop-up may show up for confirmation if Require Configuration checkbox is checked during configuration.
Once commmand is executed its ouput can be seen below the widget. Showing output is also configurable.
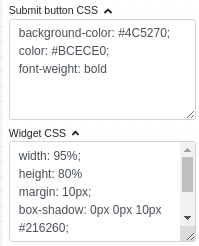
Applying CSS to widget¶
The look and feel of widgets can be customised using the Custom CSS section. CSS syntax is the same as that used for HTML files.
Above CSS rules written in the Custom Css section are applied to the widget as below: