ska-tango-examples
This project demonstrates how to structure an SKA project that provides some simple Tango devices coded in PyTango.
Installation
This project is structured to use k8s for development and testing so that the build environment, test environment and test results are all completely reproducible and are independent of host environment. It uses make to provide a consistent UI (run make help for targets documentation).
Add submodules
This project uses git submodules. In order to clone them use:
git submodule update --init --recursive
Install docker
Follow the instructions available at here.
Install minikube
You will need to install minikube or equivalent k8s installation in order to set up your test environment. You can follow the instruction at here:
git clone git@gitlab.com:ska-telescope/sdi/deploy-minikube.git
cd deploy-minikube
make all
eval $(minikube docker-env)
Please note that the command eval $(minikube docker-env) will point your local docker client at the docker-in-docker for minikube. Use this only for building the docker image and another shell for other work. This also means that when changing the shell (i.e. calling poetry shell) you should rerun this command from inside the deploy-minikube repo in order to add the relevant variables to the path.
Install ska-tango-operator
The ska-tango-operator is an extension of k8s with a Custom Resource Definition (CRD i.e. Device Server and Databaseds) and a Controller to give custom behaviours in order to have a better usage of TANGO-controls in kubernetes. You can follow the instruction at here:
git clone git@gitlab.com:ska-telescope/ska-tango-operator.git
cd ska-tango-operator
make k8s-install-chart
Install host OS dependencies
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y curl git build-essential libboost-python-dev
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py && python3 get-pip.py && rm get-pip.py
curl -sSL https://install.python-poetry.org | python3 -
Please note that:
MacOS is not supported (see MacOS users)
the above script has been tested with Ubuntu 20.04.
How to Use
Clone this repo:
git clone https://gitlab.com/ska-telescope/ska-tango-examples.git
cd ska-tango-examples
Build a new Docker image for the project:
$ make oci-build
[...]
[+] Building 111.7s (14/14) FINISHED
[...]
Install python requirements:
poetry install
Run python-test:
$ poetry shell
$ make python-test
PyTango 9.4.2 (9, 4, 2)
PyTango compiled with:
Python : 3.10.12
Numpy : 1.21.6
Tango : 9.4.2
Boost : 1.82.0
PyTango runtime is:
Python : 3.10.6
Numpy : 1.23.0
Tango : 9.4.2
PyTango running on:
uname_result(system='Linux', node='MattZenBook1', release='5.10.16.3-microsoft-standard-WSL2', version='#1 SMP Fri Apr 2 22:23:49 UTC 2021', machine='x86_64')
=================================== test session starts ====================================
platform linux -- Python 3.10.6, pytest-7.4.0, pluggy-1.2.0 -- /home/ubuntu/.cache/pypoetry/virtualenvs/ska-tango-examples-Wsi0kqW7-py3.10/bin/python
cachedir: .pytest_cache
metadata: {'Python': '3.10.6', 'Platform': 'Linux-5.10.16.3-microsoft-standard-WSL2-x86_64-with-glibc2.35', 'Packages': {'pytest': '7.4.0', 'pluggy': '1.2.0'}, 'Plugins': {'forked': '1.6.0', 'bdd': '4.1.0', 'json-report': '1.5.0', 'anyio': '3.6.2', 'repeat': '0.9.1', 'timeout': '2.1.0', 'mock': '3.11.1', 'xdist': '2.5.0', 'metadata': '3.0.0', 'cov': '2.12.1', 'nbmake': '1.4.3'}}
rootdir: /home/ubuntu/ska-tango-examples/tests
configfile: pytest.ini
plugins: forked-1.6.0, bdd-4.1.0, json-report-1.5.0, anyio-3.6.2, repeat-0.9.1, timeout-2.1.0, mock-3.11.1, xdist-2.5.0, metadata-3.0.0, cov-2.12.1, nbmake-1.4.3
collected 62 items / 6 deselected / 56 selected
[...]
======================== 56 passed, 6 deselected, 7 warnings in 120.06s (0:02:00) ========================
Python linting:
$ make python-lint
[...]
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Your code has been rated at 10.00/10 (previous run: 10.00/10, +0.00)
Helm Charts linting:
$ make helm-lint
[...]
10 chart(s) linted, 0 chart(s) failed
Install the umbrella chart:
$ make k8s-install-chart
[...]
NAME: test
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Jun 8 22:37:03 2021
NAMESPACE: ska-tango-examples
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
Test the deployment with (the result of the tests are stored into the folder charts/build):
$ make k8s-test
tar -c tests/ | kubectl run test-runner--test --namespace ska-tango-examples -i --wait --restart=Never --image-pull-policy=IfNotPresent --image=artefact.skao.int/ska-tango-images/ska-tango-examples:0.4.6-dirty -- /bin/bash -c "mkdir -p build; tar xv --directory tests --strip-components 1 --warning=all; pip install -r tests/requirements.txt; PYTHONPATH=/app/src:/app/src/ska_tango_examples KUBE_NAMESPACE=ska-tango-examples HELM_RELEASE=test TANGO_HOST=tango-host-databaseds-from-makefile-test:10000 pytest --true-context && tar -czvf /tmp/test-results.tgz build && echo '~~~~BOUNDARY~~~~' && cat /tmp/test-results.tgz | base64 && echo '~~~~BOUNDARY~~~~'" 2>&1; \
status=$?; \
rm -rf charts/build; \
kubectl --namespace ska-tango-examples logs test-makefile-runner--ska-tango-examples-test | \
perl -ne 'BEGIN {$on=0;}; if (index($_, "~~~~BOUNDARY~~~~")!=-1){$on+=1;next;}; print if $on % 2;' | \
base64 -d | tar -xzf - --directory charts; \
kubectl --namespace ska-tango-examples delete pod test-makefile-runner--ska-tango-examples-test; \
exit $status
[...]
------------ generated json file: /app/build/reports/cucumber.json -------------
------------ generated xml file: /app/build/reports/unit-tests.xml -------------
--------------------------------- JSON report ----------------------------------
JSON report written to: build/reports/report.json (99140 bytes)
----------- coverage: platform linux, python 3.7.3-final-0 -----------
Coverage HTML written to dir build/htmlcov
Coverage XML written to file build/reports/code-coverage.xml
======================== 6 passed, 56 deselected, 6 warnings in 83.80s (0:01:23) ======================================
Uninstall the chart:
$ make k8s-uninstall-chart
release "test" uninstalled
TANGO-controls examples
Basic Example
The basic example is meant to demonstrate the change event with polling on attribute.
It contains 3 devices called ‘powersupply’ (taken from here), “motor’ and ‘eventreceiver. It is contained into the package src/ska_tango_example/basic_example.
The motor uses the powersupply and generate a (random) performance value attribute which is polled (with automatic fire of the related change event). The eventreceiver receives that event.
Counter
The counter is an example of firing events with both a polled and a non polled attribute.
Teams
This package contains devices created and used by various SKA teams for testing other applications and for demonstrating concepts.
Tabata
The tabata is a realization of a gym workout (more information at here).
An example of this application can be found here.
The TANGO-controls concepts demonstrated are:
use of device properties;
handling of events coming from 5 other devices;
managing a simple state attribute (DevState and RunningState);
threading with TANGO.
The tabata device has 2 commands: Start and Stop. The start trigger the decrement on the counters to perform its job.
AsyncTabata
Same as Tabata but the realization is asynchonous.
The tabata device has 2 commands: Run and Stop. The run executes the entire job so it’s not possible to use it without an async command. The async device does not use the tango monitor, so lock is managed directly by the device.
ForAttrTabata
This is a simple device, with only forwarded attributes coming form the counters forming the tabata. It has no commands and no mocking test since forwarded attributes can be tested only with a real deployment.
Expose Tango Devices in the external network
Since v0.4.19, Tango Examples allows developers to convert Tango Kubernetes services to Loadbalancer type.
By default, this behavior is enabled if you want to deploy on Minikube by keeping the flag $MINIKUBE active.
If you want to deploy on a remote Kubernetes cluster, you must disable $MINIKUBE and enable $EXPOSE_All_DS.
The best approach is to change these flags on your local PrivateRules.mak.
Metallb
For Minikube or Openstack clusters, we depend on Metallb to expose Loadbalancer services.
Metallb is deployed and configured automatically if you use the
Deploy Minikube repository.
$ minikube addons list
|-----------------------------|----------|--------------|--------------------------------|
| ADDON NAME | PROFILE | STATUS | MAINTAINER |
|-----------------------------|----------|--------------|--------------------------------|
...
| metallb | minikube | enabled ✅ | third-party (metallb) |
...
|-----------------------------|----------|--------------|--------------------------------|
After the umbrella chart deployment, we can see the services as type Loadbalancer and the allocated external IP address.
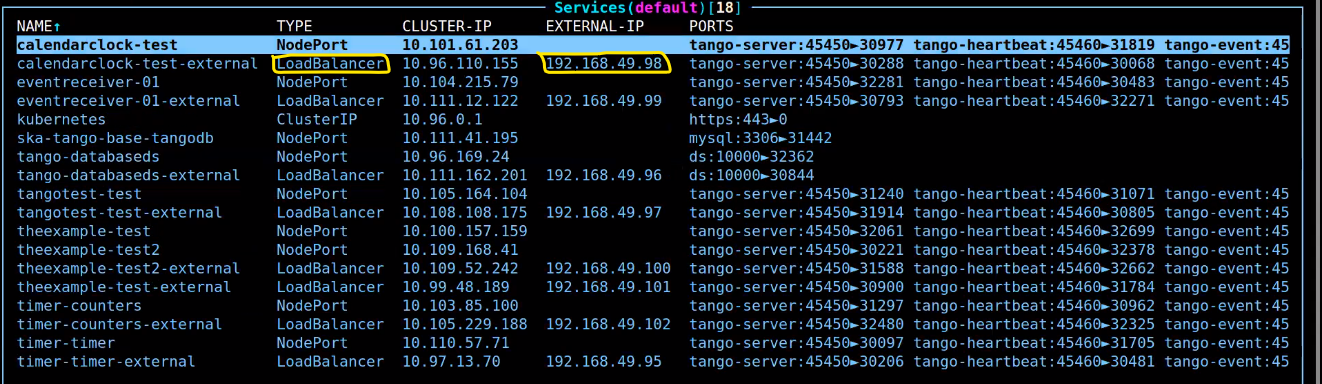
DNS
Loadbalancer Kubernetes services on Minikube
and STFC (project TechOps) have an automatic DNS resolution using an external CoreDNS deployment.
It uses the same url structure of the internal Kubernetes network <loadBalancer-svc>.<namespace>.svc.cluster.local.
You have to update the DNS configuration of your local development environment to redirect to Core DNS.
On Minikube, must run make minikube-extdns-ip on
Deploy Minikube Repository.
For the STFC cluster, you must point to Terminus (192.168.99.194).
Ubuntu
The STFC VPN automatically changes the DNS redirection on your host.
In case of any malfunction with STFC VPN DNS or working with Minikube,
we need to update the systemd-resolved config /etc/systemd/resolved.conf.
[Resolve]
DNS=<dns-ip-address>
Domains=~svc.cluster.local
WSL
For newer versions of WSL2, systemd is available, by editing /etc/wsl.conf as follows:
...
[boot]
systemd=true
...
Followed by wsl --shutdown and then, wsl to restart it again, in Powershell.
If your WSL does not have systemd, any changes on systemd-resolved are not applied.
One workaround is to delete the file /etc/resolv.conf and create a new one.
The external CoreDNS IP goes on the first line, and any public DNS of your choice in the following line(s).
nameserver <extdns ip>
nameserver 8.8.8.8 # Google DNS
nameserver 1.1.1.1 # Cloudfare DNS
These DNS configuration files are recreated on every startup (point to Windows host DNS),
so we need to add a variable on the WSL settings /etc/wsl.conf to disable that.
...
[network]
generateResolvConf = false
...
Finally, shutdown WSL on PowerShell wsl --shutdown and then, wsl to restart it again.
TANGO References
https://pytango.readthedocs.io/en/stable/contents.html
https://pytango.readthedocs.io/en/stable/green_modes/green_modes_server.html
https://pytango.readthedocs.io/en/stable/testing.html
https://pytango.readthedocs.io/en/stable/client_api/index.html
https://pytango.readthedocs.io/en/stable/server_api/server.html
ska-tango-images
Please note that this project make use of the charts and docker images for the TANGO-controls framework available at here.
Test execution
All tests created for the present project can run in simulated mode or in a real environment except for the ones marked as post_deployment.
make k8s-test runs all the application test procedures defined in the folder tests in a new pod in the k8s deployment. This target copies the tests folder into a new pod and execute the test with the option --true-context allowing the execution to happen against the real application. On success it copies the resulting output and test artefacts out of the container and into the folder charts/build directory, ready for inclusion in the CI server’s downloadable artefacts.
make python-test runs the application test procedures (except the ones marked as post_deployment) defined in the folder tests without starting a new pod. The result will be found in the build.
Debugging with vscode
In order to debug a device server, this project uses the library debugpy. To be able to debug your code, just run the following command:
$ kubectl port-forward pod/tabata-tabata-0 12345:5678 -n ska-tango-examples
The above command will create a port forwarding between the local machine and the event receiver pod.
Once done open the Run tab on vscode and press the debug button which correspond to the launch.json configuration file Python: Remote Attach.
The .vscode folder contains also the settings to be able to run the pytest with the python extension. Note that it expects that a venv folder is present.
Makefile targets
This project contains a Makefile which acts as a UI for building Docker images, testing images, and for launching interactive developer environments.
For the documentation of the Makefile run make help.
MacOS users
The Python binding for TANGO-controls framework does not work out of the box in MacOS. However MacOS users can still use this repository for development.
The TANGO-controls framework is needed only for unit-testing (make python-test) to provide debugging capability and, together with the unit-testing target it is also provided another target in the Makefile to make the same run inside a container (in this case no debug capability are available).
Run python-test with:
$ make pipeline_unit_test
Unable to find image 'artefact.skao.int/ska-tango-images-tango-itango:9.3.4' locally
9.3.4: Pulling from ska-tango-images-tango-itango
[...]
PyTango 9.3.3 (9, 3, 3)
PyTango compiled with:
Python : 3.7.3
Numpy : 1.19.2
Tango : 9.3.4
Boost : 1.67.0
PyTango runtime is:
Python : 3.7.3
Numpy : 1.19.2
Tango : 9.3.4
PyTango running on:
uname_result(system='Linux', node='6c992e221a42', release='4.19.128-microsoft-standard', version='#1 SMP Tue Jun 23 12:58:10 UTC 2020', machine='x86_64', processor='')
================================================================================================== test session starts ===================================================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.7.3, pytest-6.2.4, py-1.10.0, pluggy-0.13.1 -- /usr/bin/python3
cachedir: .pytest_cache
metadata: {'Python': '3.7.3', 'Platform': 'Linux-4.19.128-microsoft-standard-x86_64-with-debian-10.9', 'Packages': {'pytest': '6.2.4', 'py': '1.10.0', 'pluggy': '0.13.1'}, 'Plugins': {'bdd': '3.4.0', 'asyncio': '0.15.1', 'ordering': '0.6', 'timeout': '1.4.2', 'repeat': '0.9.1', 'xdist': '2.3.0', 'forked': '1.3.0', 'mock': '3.6.1', 'cov': '2.12.0', 'metadata': '1.11.0', 'pylint': '0.18.0', 'pycodestyle': '2.2.0', 'pydocstyle': '2.2.0', 'json-report': '1.3.0'}}
rootdir: /home/tango/ska-tango-examples, configfile: setup.cfg, testpaths: tests
plugins: bdd-3.4.0, asyncio-0.15.1, ordering-0.6, timeout-1.4.2, repeat-0.9.1, xdist-2.3.0, forked-1.3.0, mock-3.6.1, cov-2.12.0, metadata-1.11.0, pylint-0.18.0, pycodestyle-2.2.0, pydocstyle-2.2.0, json-report-1.3.0
collected 54 items / 6 deselected / 48 selected [...]
- generated json file: /home/ubuntu/ska-tango-examples/build/reports/cucumber.json --
- generated xml file: /home/ubuntu/ska-tango-examples/build/reports/unit-tests.xml --
--------------------------------- JSON report ----------------------------------
JSON report written to: build/reports/report.json (165946 bytes)
----------- coverage: platform linux, python 3.8.5-final-0 -----------
Coverage HTML written to dir build/htmlcov
Coverage XML written to file build/reports/code-coverage.xml
======================== 48 passed, 5 deselected in 42.42s ========================
Windows Users
The preffered way for using this repository on windows is with the help of WSL. The procedure described here is tested with WSL Ubuntu 20.04. To be able to open GUI applications, it is needed an X server running like VcXsrv X Server.
Running GUIs
Note: your Xserver needs to allow TCP connections. This will be different for each window manager, but on Ubuntu 20.04 using gdm3 it can be enabled by editing /etc/gdm3/custom.conf and adding:
[security]
DisallowTCP=false
In order for these changes to take effect you will need to restart X (it’s just easier to reboot).